Of course there’s a lot of other things to talk about the Mantis Shrimp. But today, I’m going to only talk about its eyes.
Colours
The eyes of a Mantis Shrimp are one of the most advanced eyes on the planet. To realize how extraordinary their colour vision is, you need to have some perspective on what we are talking about.
Colour is just a trick of our mind. What we see is really out there, there’s no way to know for sure if it is the reality. Or, there’s no way for us to explain what we really see.
For instance, imagine how we see the world, say particularly, the colour red and all its derived colours. Now, what you see is very different from how a colour blind person or a dog sees it. Dogs and about 10% of men who are colour blind can’t see colours like we do. That is because, instead of 3 cones (red, blue and green sensitive ones), they just have two. If you and a dog would point their eyes towards the same rainbow, both of you would see a very different image (if you are not colour blind).
A dog probably would see a rainbow which would start with a blue colour and then there’d be green in it for a dog. Nothing else. That is because it has no red sensitive cones. A single difference in the number of types cones can make such a huge difference in the colour vision. Addition of the single red sensitive cone enables us to see a whole set of new colours.
Some women (estimated to be about 2-3%of the world’s population!) have a super-human ability that makes them able to see a whole set of new colours. Like we see a million different colours, these women can probably see 100 Million different colours. It’s hard to imagine what they really see. Probably that is why they say men are so bad at colours.
Similarly, consider a butterfly. They have 5-6 different kinds of cone receptors. So, when they look at a rainbow, they probably see a range of colours between the blues and the greens and the greens and the yellows. Of course, it can also see an ultraviolet beyond the violet. Incredible enough.
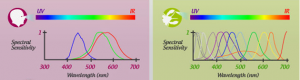
The Mantis Shrimp, an animal of the size of your finger, has one of the most amazing colour visions. It has 16 different types of cones. You can’t even start to imagine how the world looks to them. And suppose they try and see a rainbow, they’d see a really rich set of colours. No other animals we know have even a visual system that is half as advanced. There’s no reason they must have this ability.16 is just too many cones!
Needless to say, these technological marvels can see ultra-violet light, infra-red light, and some can even see polarised light.
Hexnocular vision

Now, we see with our two eyes and call it a binocular vision. We have 2 eyes and 1 focal point each. So, to see in 3-D, we need both out eyes.
Mantis Shrimp, however, has 2 eyes with 3 focal points each. Each of its eye is divided into 3 sections and can see 3 different images, using the 3 different sections. It doesn’t need 2 eyes to see in 3-D. One is enough. Besides that, it is able to judge depth much better than we are able to do it. Think of an image stitched out of 6 different eyes.