You can skip everything under this subheading
Note: In the past, I’ve been requested by my readers to keep the articles on AweSci short. It made sense. Since I write one article everyday, for readers, it definitely is easier to read and digest a smaller article, day in and day out. Thanks to the rate at which short attention span is being nurtured by the internet, not all have the appetite to take in bigger pieces everyday.
I see it this way – doing a very little thing everyday religiously, compounds. It makes a huge difference in your life. Even devoting 2 minutes a day for a single thing makes big changes over time. Here, I’m doing more than an hour everyday! If you read these daily, you are devoting around 10 minutes a day to learn something. You’ll do great in life!
At the same time, smaller articles of about 300-500 words are good for me too. By sticking to smaller ones, I can accomplish my own goal of learning and writing about one new thing everyday, by doing less. Also, composing smaller articles doesn’t take a lot of time which allows me to take care of the primary daily activities.
However, today, a reader asked me about the decreasing length of my articles. It’s so good to know that readers actually care about these things. Nevertheless, as explained above, there’s nothing wrong in it, but it did make me think about what was causing it? Well, I’ve been busy with so much stuff for the past few days, I don’t have partners for the blog and it’s tough doing it alone. Still, with all the travelling and full day outings in a 40 degree sun for the past few days, I managed at least one article a day. Pat on the back to me for being able to do that.
Anyway, the point is that articles don’t have to be long. For the question my faithful reader asked me, I needed to write this to explain it to him. He deserves a good explanation for being faithful reader to my little blog. If I learn something and sleep a little bit smarter than the last day, I’ve accomplished my goal for the day. That way, the purpose of you reading this is served. That way, the purpose of the blog is served.
What do you say, long or short? Or, you are always welcome if you want to contribute on this blog. We have hundreds of people who’d come by daily to read your article!
Background
In the past, we’ve seen how geniuses at MIT have figured out a way to capture the beam of light on video, and have replayed it moving in slow motion. In simple words, moving light was captured on camera. Something which the human eye had never seen before was shown moving with the help of technique. But, then there are other invisible things too. Like sound!
Watching sound
Watching the iTunes visualization go, isn’t equivalent to watching sound. Visualizations and waveforms are merely a digital depictions of sound.
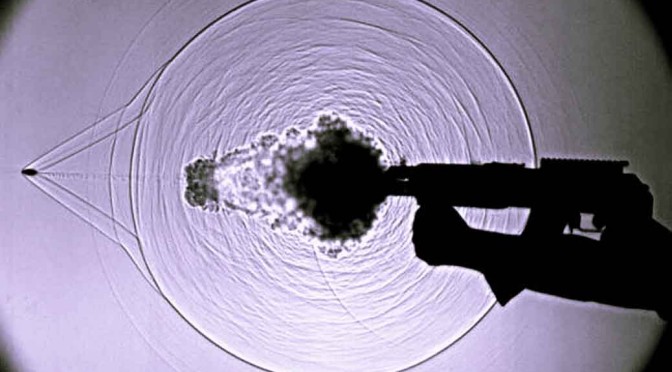
While listening to sounds can be too easy, seeing it with your eyes isn’t natural. For that, there is camera trick that can be used to see the actual sound waves travelling in the air. In fact, with this technique, any disturbance in the air can be seen which otherwise, would be totally invisible to the naked eye. It let’s you see sound!
The camera technique has a fairly confusing name. It’s called Schlieren flow visualization. But that shouldn’t confuse you because in simple words, with this technique it is possible to capture on film, the disturbances that are caused by things moving in the air. For example, the invisible disturbances that are caused in the air (a transparent medium) when someone claps can be made visible by using the technique – Schlieren flow visualization.
Here is how it works
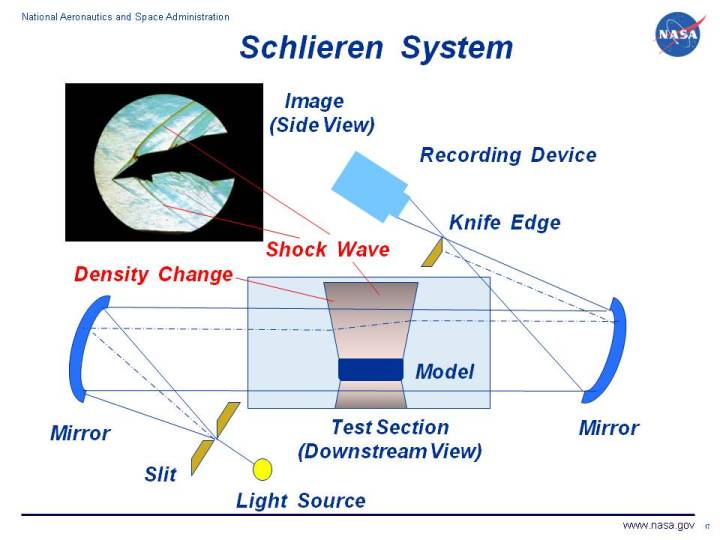
If I write it in words, I’ll only confuse you more. So, here is an NPR video that explains the mechanism very accurately. Otherwise, there’s always this NASA page for it.
Amazingly, like the video shows, it can be used to see the heat coming off the human body. Now, I can definitely think of some creative applications for that.