By Anupum Pant
Background
If you consider the habits, social organization, communities, network of roadways, possession of domestic animals, and counting skills of ants, they are not very different from humans. Yes, ants even domesticate animals. And we’ve talked about their counting skills in the past. Then, I came across a very interesting experiment sir John Lubbock decided to do on ants.
Experiment
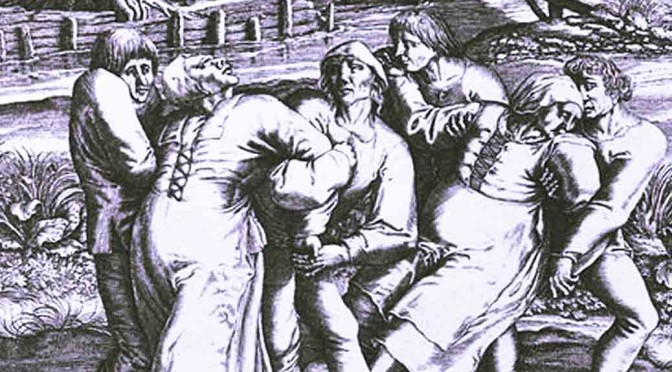
He had in his captivity a number of varieties of ants living in different colonies. One day he saw a group of ants feeding on honey together. He picked twenty five of them and managed to intoxicate them by some method, others were left there, feeding on honey.
Next, he picked twenty five other ants of the same species, from a different colony and intoxicated them too. He then placed all of these 50 intoxicated ants near the honey, in the path which the ants were using to move to and fro from the honey.
He watched them for hours and it was an amazing thing he found. The twenty five ants which belonged to the same colony of ants that were feeding on honey were treated much differently by them, than the other 25 ants of the same species that belonged to a different nest! Somehow they were able to identify the ants of their own nest – differentiate friends from strangers.
Twenty out of the twenty five friend ants (which belonged the same nest) were carried by the honey feeding ants to their home. While about 18 of the other intoxicated stranger ants were picked up and thrown into water.
There were just 5 friend ants which were thrown into water (probably accidentally) and 6 stranger ants which were carried back to home (probably accidentally, again)
Nevertheless, most ants were correctly identified as friends and strangers. Moreover, I think their reaction to drunk friends and drunk strangers was so much like what human beings would do!
Next Experiments
In an experiment which he did later, the researcher tried separating friend ants (of the same nest) for about 4 months. And when they met after 4 months they were able to clearly identify each other. They caressed each other with their antennae.
In other experiments when he introduced a stranger ants in a nest, the strangers were evicted immediately and sometimes even killed.
There are a couple of other interesting experiments he has mentioned in his article here. Do read it whenever you find time. [link]