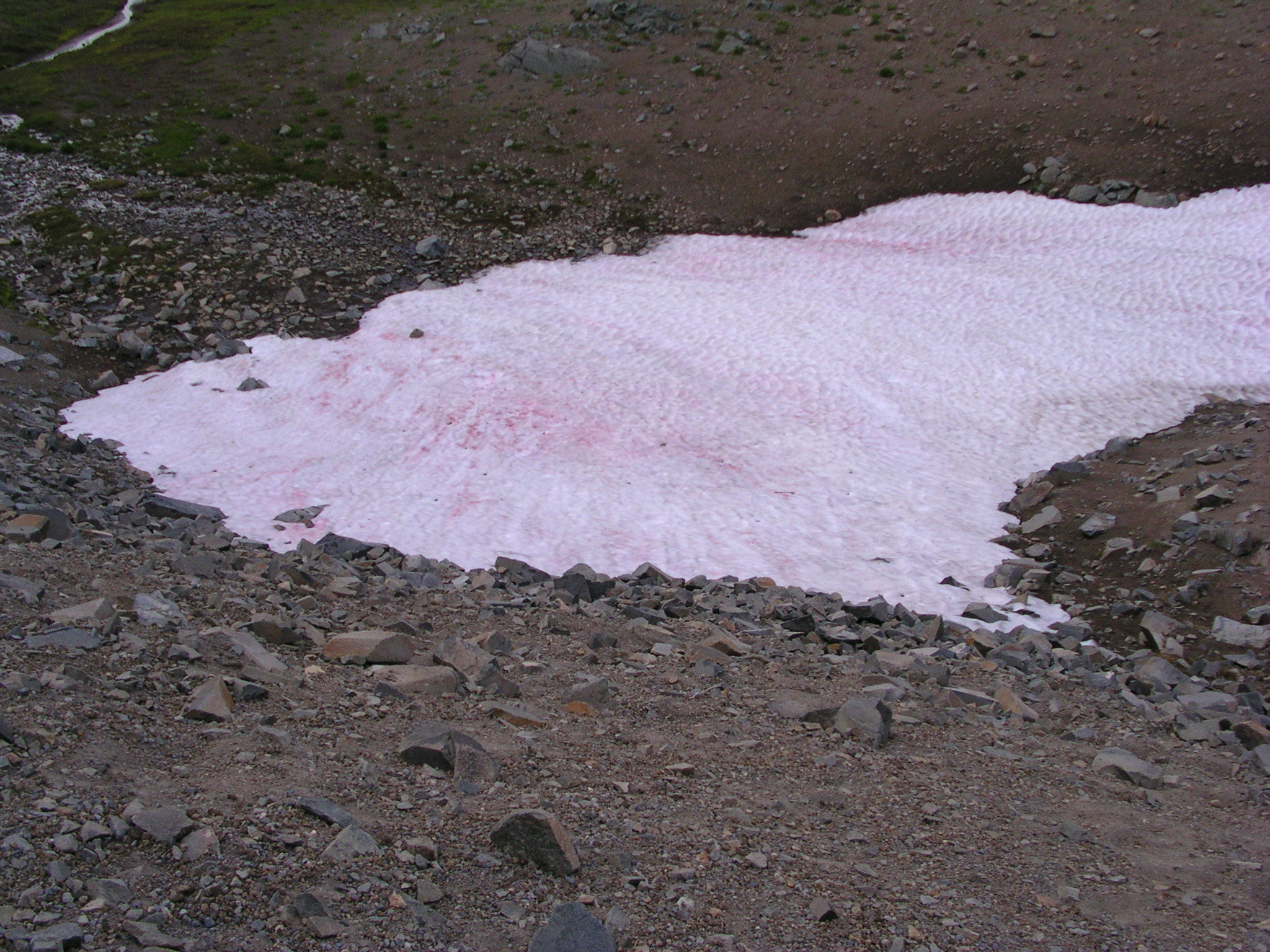
What is Watermelon Snow?
Watermelon Snow, exactly as the name suggests, is a pink colored watermelon slushy like snow. It has been spotted in a number of snow covered regions of the earth which are permanently covered with snow. Although the pink color may look like it comes from some sort of a mineral deposit, or some other inorganic source such as meteorite debris, interestingly it is due to living organisms – Algae. Its other names are – snow algae, pink snow, red snow, or blood snow.
How does it get that color?
One of the widely found algae species in these pink snow patches contains a red pigment (called carotenoids) in addition to the green chlorophyll component. The alage itself is called Chlamydomonas nivalis.