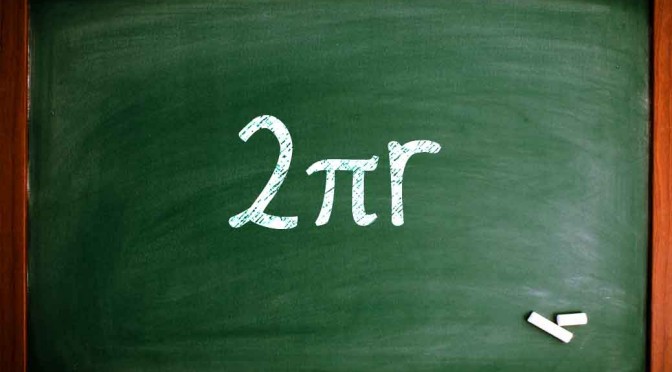By Anupum Pant
Background
Couple of days back, I read about a puzzling geometrical conundrum, probably on Quora. It might not sound amusing to you math geeks out there, but to me, it sounded like an impossible thing at first. The sad part is, I did not save the source link in my notes. Thankfully, I did care to note down the idea. Let me call it the “Thread wound Around the Earth” puzzle.
Here is a simple question first. Try answering it without any calculation. Just guess. Be honest to yourself, don’t see the answer just below it. Scroll slow.
As BBC’s website puts it…
Imagine a piece of string wrapped around the Earth’s equator – that’s about 40,000km. How much MORE string would you need for it to sit 15cm above the ground, all the way around?
A) 1 metre, B) 1 kilometre or C) 1,000 kilometres
Thread wound around the Earth
The answer is A) 1 meter. Yes, just 1 meter of extra rope.
Suppose, you have an outrageously long thread with you. You tie it around the base of a tree, somewhere at the equator. Now, you go around the earth, along the equator, carrying the thread with you, till you come back to that tree where you started. At this point, you’ll have a thread that goes around the earth in a circle. At every point, let us imagine that the rope is taut and touching the ground (there are no mountains or valleys in between). It’s a perfect circle (assume).
Suppose, you still have an extra meter of the rope left now. So, you break the wound rope at one point and add the extra meter to it. That of course slackens the wound rope. For this rope to be taut again, it has to be lifted up by some amount. What do you think that distance would be from the ground? Assume that the rope still makes a huge circle just above the ground and lifts by equal amount at every point along the equator.
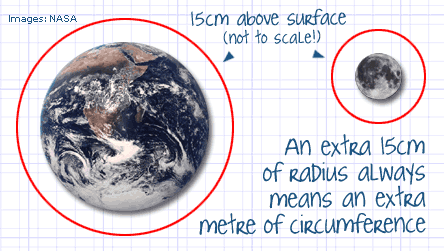
Just the extra meter of rope, causes the rope to rise by ~15 cm all around the earth (actually 15.9 cm). For a single meter of rope added to a 40,000 km of rope, that sure seems like a huge lift! But that isn’t all…
The most amazing part is that, no matter what the size of the circle, a meter of increased circumference will increase the radius by ~15 cm. Always!
Try tying a rope around a golf ball, or even try doing that around the sun. It’s always that – 1 meter increase in circumference, always increases the radius by ~15 cm.
The Math is so straightforward.
If you think about it mathematically, it is completely straightforward.
Radius X 2 X Pi = Circumference
That means, the Radius is directly proportional to the circumference of a circle. Everyone knows that. So, the amount of change in the radius is reflected proportionally in the circumference, the magnitude of radius can be anything, really. So it’s pretty natural that just a single meter of rope is required to lift the rope by 15.9 cm around any circle. The size doesn’t matter. But practically thinking, the above question makes it seem impossible.
Please hit like if you learnt something from the article.